
Sudo update update#
If you don’t use the update command, you won’t refresh the cache, which would not give you a clue about the available package updates. 1.It is prudent to take a backup of all your databases and files before embarking on any major upgrade of an operating system. The metadata includes information pertaining to the version, repository, dependency, and other relevant package details.
Sudo update software#
Your Linux system has an available cache of software (packages), which contains the necessary metadata related to those packages. Avoid starting Postman using the sudo command, as it will create permission issues on. On the other hand, the apt upgrade command downloads and installs available updates on your machine in one go. This will ensure that future updates can be installed correctly.
Sudo update install#
The update command gives you an idea about the available updates, but it does not download or install the updates within your distro. apt upgrade: A ComparisonĮven though the apt update command might seem like the obvious go-to option to update your packages on Linux, it’s not entirely the case. But the point is, what's the difference between these commands, and how can you use them to update your Linux packages? apt update vs. From the terminal itself it is much faster and. Whilst it is unlikely that data will be lost during the upgrade process, it’s better to be safe than sorry. Also ensure that all of your user data has been backed up.
Sudo update password#
From your terminal, entering your password and pressing Y when prompted. You can choose to keep them, but by default it’s okay to click Remove to progress.ĭespite the warning that removing packages can take several hours, this is extremely unlikely and after a minute or two you will be prompted to restart your system to complete the upgrade.When looking for ways to update packages, you will come across commands like apt update, apt upgrade, and related versions. sudo apt-get update to update the list of repositories, and then sudo apt-get upgrade to update the system. Before proceeding ensure that your software is up to date by running: sudo apt update. Once the newest packages have been installed you’ll be prompted to remove the obsolete packages from the previous Ubuntu release. sudo apt-get update This command refreshes your local list of software, making a note of any newer revisions and updates. To prevent the OS locking during the process, the lock screen will be disabled. If you launched an EC2 instance that uses an Amazon Linux 2 AMI into an IPv6-only subnet, you must connect to the instance and run sudo amazon-linux-https. Ensure you are running the server on UPS or your laptop battery is fully charged.
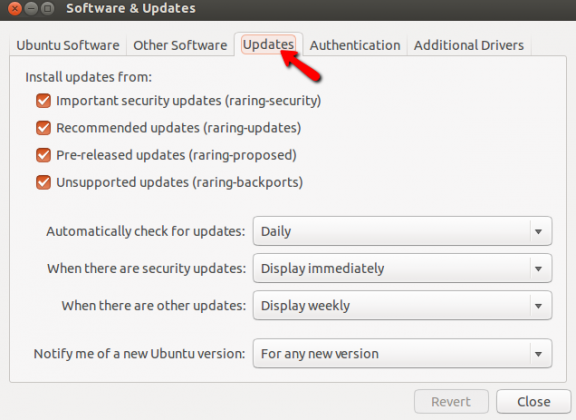
Please do not cancel the operation once started, as it will leave your Ubuntu machine in an inconsistent state. This will take you to an overview window showing you the progress of the upgrade.Īs this progresses through the stages you will receive some additional prompts to progress once the upgrade requirements have been gathered. The upgrade process takes its sweet time due to the speed of the internet and other factors. First you will see a link to the release notes for the target release, detailing the newest features, improvements and known issues. What is the meaning of the command sudo apt upgrade sudo apt upgrade is the command used to download any available updates and apply them to the out-dated packages installed in a Linux system.

We explain how the sudo apt update command works in this brief guide. Some older tutorial also mention sudo apt-get update and sudo apt-get upgrade. Follow the upgrade flowįrom this point on, the upgrade UI will guide you through the process. The sudo apt update command is one of the first commands a Linux newbie learns to use. 5 min read If you want to keep your Ubuntu or Debian system updated, you use the combination of sudo apt update and sudo apt upgrade commands.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
